Product Description
Product Description
We(HangZhou BST) export construction machinery parts, specializes in the manufacturing and supplying of Shantui, Cat and komat su parts for over 15 years. Our company has a complete range such as engine parts ,transmission parts,hydraulic parts, electrical parts,drive parts,undercarriage parts, filter. Models such as komats D60/80/155,PC2
175-15-42322
09232-5715
571-5715
175-15-41140
706-7L-01110
209-27-00160
209-27-71370
21n-27-31330
209-27-61360
198-09-31630
209-27-71521
21n-27-31310
21n-27-31110
209-27-71330 Spitter
209-27-71261
207-27-61230
20Y-27-21250
209-27-71480
20Y-27-21290
209-27-71141
209-27-71410
21n-27-31250
209-27-71390
21n-27-31260
208-27-61350
20y-27-21240
209-27-71350
20G-26-11240
209-27-71310
20Y-27-21280
21n-27-31120
21n-27-31210
21n-27-31221
21n-27-00150
21n-27-31120
21n-09-31120
209-38-73360
06030-06219
06030- 0571 4
04070-00140
209-38-73170
07002-22434
07030-03034
07005-03016
209-38-73130
209-38-73140
06000-23124
07000-15335
21n-26-31140
208-26-52263
208-26-61291
21n-26-31110
20Y-27-21250
208-26-63140
207-27-63210
207-27-63230
20y-27-13310
208-26-63131
207-26-61180
207-27-63250
20Y-27-11250
208-26-63110
208-26-61151
20Y-27-22210
| Part name | Part No. | Des |
| Shantui Alternator | 4060811 | Shantui dozer parts |
| Shantui Alternator | 3016627 | Shantui dozer parts |
| Shantui Alternator | 4061007 | Shantui dozer parts |
| Shantui Alternator | VG1095094002 | Shantui dozer parts |
| Shantui Alternator | 6N9294/5S9088 | Shantui dozer parts |
| Shantui Alternator | D11-102-13 | Shantui dozer parts |
| Shantui Alternator | 13571500/4110000054053 | Shantui dozer parts |
| Shantui Alternator | 13571345/411000571005 | Shantui dozer parts |
| Alternator | JFZ279 | 28V 70A |
| Alternator | JFZ273 | 28V 70A |
| Alternator | JFZ276 | 28V 70A |
| Alternator | AVI136 series | 28V 70A |
| Alternator | AVI144 series | 28V 100A/14V 150A |
| Alternator | JFZ210/211 series | 28V 100A-110A |
| Alternator | 8LHA3096UC | 28V 110A |
| Alternator | 8LHA3040UC | 28V 120A |
| Alternator | 8SC3141VC series | 28V 140A-150A |
| Alternator | AC172RA series | 28V 140A |
| Alternator | AVi168A series | 28V 150A |
| Alternator | AVi168W series | 28V 150A |
| Alternator | AVi168F3001 | 28V 150A |
| Alternator | 8SC3239VC series | 28V 150A |
| Alternator | 8SC3238VC series | 28V 150A |
| Alternator | 8SC3110VC series | 28V 150A |
| Alternator | AVi147 series | 28V 120A |
| Alternator | AVi147 series | 28V 120A |
| Alternator | AVE2119-E | 28V 110A |
| Alternator | AViC2002C | 28V 70A |
| AOBO series | ||
| Alternator | JFZ2922 | 28V 55A |
| Alternator | JFZ2200C | 28V 70A |
| Alternator | JFZ2971A | 28V 75A |
| Alternator | JFZ2971B | 28V 75A |
| Alternator | JFZ2971D | 28V 75A |
| Alternator | JFZ2150 | 28V 150A |
| Alternator | HOWO | 28V 80A |
| Alternator | HOWO3000 | 28V 80A |
| series | ||
| Alternator | CA1666IR | 28V 80A |
| Alternator | CA1693IR | 28V 110A |
| Alternator | CA1148IR | 28V 80A |
| Alternator | CA907IR | 28V 80A |
| Alternator | CA550IR | 28V 55A |
| Alternator | CA1593IR | 28V 80A |
| Alternator | CA1699IR | 28V 80A |
| Alternator | CA853IR | 28V 80A |
| Alternator | CA1236IR | 28V 140A |
| Alternator | CA1237IR | 28V 140A |
| Alternator | CA1853IR | 28V 80A |
| Alternator | CA1883IR | 28V 110A |
| DENSO series | ||
| Alternator | DENSO series | 28V 95A |
| Alternator | DENSO series | 14V 130A |
| Alternator | Delco 24SI series | 28V 70A |
FAQ
Q1:You are a trader or manufacturer .
We are a trader .
Q2: How about the payment terms ?
We usually accept T/T . Other terms also could be negotiated .
Q3: Warranty
3-6 months warranty. If any parts break during the warranty, Just offer us the proof . We’ll send you a new 1 !
Q5:If parts be lost during delivery , how solve ?
We’ll resend the parts free of charge .
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Type: | Crawler |
| Application: | Excavator |
| Certification: | ISO9001: 2000 |
| Condition: | New |
| Samples: |
US$ 10/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
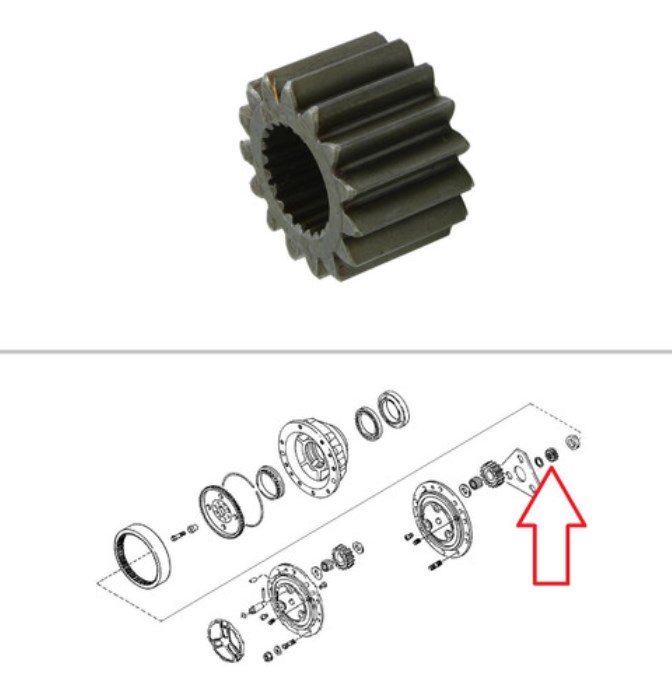

How does the size of a sun gear affect the gear ratio in planetary systems?
The size of the sun gear plays a significant role in determining the gear ratio in planetary gear systems. The gear ratio determines the relationship between the input speed and torque and the output speed and torque in the system. Here’s an explanation of how the size of the sun gear affects the gear ratio in planetary systems:
- Direct Proportion:
In a planetary gear system, the gear ratio is influenced by the relative sizes of the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear. The gear ratio is typically expressed as the ratio of the output speed to the input speed or the ratio of the output torque to the input torque.
When considering the size of the sun gear, it is important to understand that the gear ratio is inversely proportional to the size of the sun gear. In other words, as the size of the sun gear increases, the gear ratio decreases, and vice versa.
- Power Distribution:
The size of the sun gear affects the power distribution within the planetary system. As the sun gear rotates, it engages with the planet gears, which, in turn, mesh with the ring gear. The interaction between these gears determines the gear ratio.
A larger sun gear allows for a higher number of teeth on the sun gear itself as well as on the planet gears. This means that each rotation of the sun gear will result in a smaller rotation of the planet gears and the ring gear. Consequently, a larger sun gear leads to a lower gear ratio, reducing the output speed and increasing the output torque.
- Torque Amplification:
Another factor influenced by the size of the sun gear is torque amplification. In planetary gear systems, the sun gear’s size affects the torque multiplication or reduction capabilities of the system.
With a larger sun gear, the system can provide higher torque output for a given input torque, resulting in torque amplification. This can be advantageous in applications where increased torque is required, such as during vehicle acceleration or heavy load conditions.
Conversely, a smaller sun gear reduces the torque output of the system, resulting in torque reduction. This can be useful in situations where a lower torque output is desired, such as when precise control is required or when operating in low-torque applications.
- Overall Gear Ratio Range:
The size of the sun gear also affects the overall gear ratio range that can be achieved in a planetary system. By varying the size of the sun gear relative to the other gears, different gear ratios can be achieved, allowing for a wider range of output speeds and torques.
For example, if a system requires a higher gear ratio range, a larger sun gear can be used in combination with appropriately sized planet gears and a ring gear. Conversely, if a lower gear ratio range is desired, a smaller sun gear can be employed.
It’s important to note that the size of the sun gear alone does not determine the gear ratio. The gear ratio is influenced by the combination of the sizes of all the gears within the planetary system.
In summary, the size of the sun gear in a planetary gear system has a direct impact on the gear ratio, power distribution, torque amplification, and overall gear ratio range. A larger sun gear results in a lower gear ratio, while a smaller sun gear leads to a higher gear ratio. The size of the sun gear, along with the sizes of the other gears, determines the performance characteristics of the planetary system.
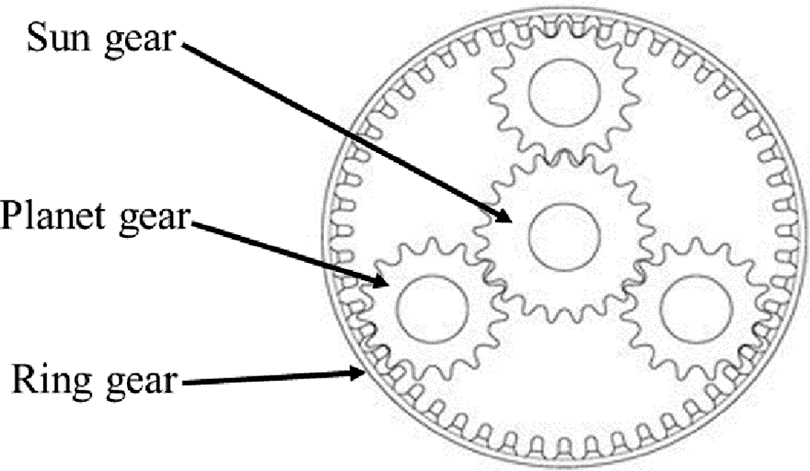
How does a sun gear handle variations in load and speed conditions?
A sun gear is designed to handle variations in load and speed conditions in mechanical systems. Its unique positioning and interaction within a planetary gear arrangement contribute to its ability to adapt to changing load and speed requirements. Here’s an explanation of how a sun gear handles variations in load and speed conditions:
- Load Distribution:
In a planetary gear system, the sun gear is located at the center and engages with multiple planet gears, which in turn interact with the outer ring gear. This configuration enables the sun gear to distribute the load among the planet gears. As the load on the system varies, the distribution of load among the planet gears adjusts accordingly. The load distribution mechanism allows the sun gear to handle variations in load conditions by effectively sharing the load across multiple contact points.
- Torque Amplification:
The arrangement of the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear in a planetary system allows for torque amplification. By changing the number of teeth on the gears and their relative sizes, the gear ratio can be customized. This capability enables the sun gear to adapt to variations in load and speed conditions. When higher torque is required, the gear system can be configured to provide torque amplification by increasing the gear ratio. Conversely, when lower torque is needed, the gear ratio can be adjusted accordingly. This flexibility in gear ratio configuration allows the sun gear to handle variations in load and speed by adapting the torque output.
- Speed Regulation:
Another way the sun gear handles variations in load and speed conditions is through speed regulation. In a planetary gear system, the sun gear’s rotation speed is determined by the input speed and the gear ratio configuration. By adjusting the gear ratio, the rotational speed of the sun gear can be controlled. This speed regulation capability allows the sun gear to adapt to changing speed requirements. When higher speeds are necessary, the gear ratio can be adjusted to increase the rotational speed of the sun gear. Similarly, when lower speeds are desired, the gear ratio can be modified accordingly. The sun gear’s ability to regulate its rotational speed enables it to accommodate variations in load and speed conditions.
- Sturdy Construction:
Sun gears are typically constructed from durable materials such as hardened steel or other high-strength alloys. This robust construction enables them to withstand the forces generated by variations in load and speed conditions. The sturdy design of sun gears ensures that they can handle the stresses and strains associated with changing operating conditions without experiencing premature wear or failure.
In summary, a sun gear handles variations in load and speed conditions through load distribution among the planet gears, torque amplification or reduction based on the gear ratio configuration, speed regulation by adjusting the gear ratio, and its sturdy construction. These features enable the sun gear to adapt to changing requirements, ensuring reliable and efficient operation in various mechanical systems.
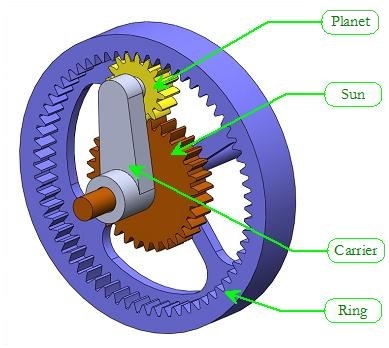
How does a sun gear affect the overall gear ratio in a system?
The presence and characteristics of a sun gear play a significant role in determining the overall gear ratio in a system. Understanding how the sun gear affects the gear ratio helps in analyzing and designing gear systems with the desired performance. Here’s an explanation of how a sun gear affects the overall gear ratio in a system:
- Number of Teeth: The number of teeth on the sun gear influences the gear ratio. In a simple gear system, where the sun gear engages with a single gear, the gear ratio is determined by the ratio of the number of teeth on the two gears. For example, if the sun gear has 10 teeth and the other gear has 30 teeth, the gear ratio would be 1:3, meaning the output gear rotates three times slower than the sun gear.
- Arrangement with Other Gears: In more complex gear systems, such as planetary gear configurations, the arrangement of the sun gear with other gears further influences the gear ratio. In a planetary gear set, the sun gear engages with multiple planet gears and an outer ring gear. By manipulating the sizes and arrangements of these gears, a wide range of gear ratios can be achieved. For instance, if the sun gear is fixed, the ring gear becomes the output and the gear ratio is determined by the relative sizes of the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear.
- Planet Gears: The number of planet gears in a planetary gear system also affects the gear ratio. Increasing or decreasing the number of planet gears alters the gear ratio by changing the load distribution and the interaction between the sun gear and the ring gear. More planet gears generally result in a higher gear ratio, while fewer planet gears tend to reduce the gear ratio.
- Epicyclic Gear Trains: The arrangement of gears in an epicyclic gear train, which includes the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear, allows for even more complex gear ratios. By fixing or holding certain gears while others are driven, various gear ratios can be achieved. For example, fixing the ring gear and driving the sun gear produces a different gear ratio compared to fixing the sun gear and driving the ring gear.
- Variable Gear Ratio: In some systems, the gear ratio can be varied by changing the position or speed of the sun gear. This can be achieved using mechanisms such as adjustable clutches or continuously variable transmissions (CVTs). By modifying the engagement between the sun gear and other gears, the gear ratio can be adjusted to optimize performance for different operating conditions.
In summary, the presence and characteristics of a sun gear, including the number of teeth, its arrangement with other gears, the presence of planet gears, and the overall gear system configuration, all contribute to the determination of the gear ratio. Understanding these factors allows for the design and control of gear systems with specific gear ratios to meet the requirements of various mechanical applications.


editor by CX 2023-09-08